Patient Education
Blepharitis
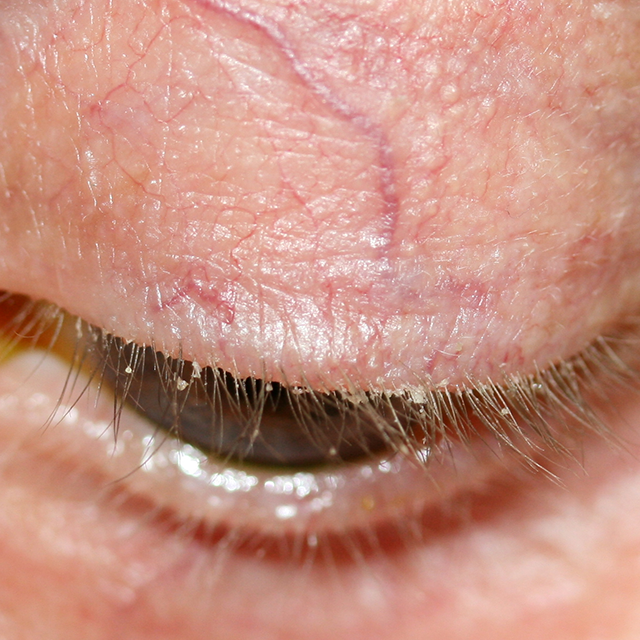
Blepharitis
Blepharitis refers to inflammation of the eyelids, particularly at the lid margins. It is a common disorder and may be associated with a low-grade bacterial infection or a generalized skin condition (eg. acne rosacea).
Blepharitis can be classified into 3 types: Anterior blepharitis, posterior blepharitis, and mixed (anterior and posterior).
- Classifications
- Symptoms
- Complications
- Treatment
- Anterior Blepharitis
Anterior blepharitis involves the outside of the eyelid, particularly along the base of the eyelashes. Symptoms include burning, grittiness, and crusting and redness of the lid margins. These symptoms are usually worse in the mornings and are characterized by remissions and exacerbations.
- Posterior Blepharitis
Posterior blepharitis is manifest as meibomian gland dysfunction and affects the inner eyelid. This can be caused by acne rosacea, and results in excessive meibomian gland secretions. Signs and symptoms may include an oily, foamy froth at the lid margins, thickened and red lid margins.
- Eye irritation
- Burning
- Tearing
- Grittiness
- Crusting around the lashes
- Red lid margins
- Ocular dryness
- trichiasis - misdirected eyelashes
- madarosis - loss of eyelashes
- distichiasis - abnormal growth of lashes from the orifices of the meibomian glands
- entropion - eyelid folds inward
- ectropion - eyelid folds outward
- internal hordeolum - "stye"
- tear film instability
- Ocular dryness
Eyelid hygiene is the cornerstone of treatment for most cases of blepharitis, and consists of the following steps:
- Wash your hands, then dampen a clean washcloth with warm water
- Apply this warm compress to the eyelids
- Cleanse the eyelids with a commercial lid scrub or baby shampoo diluted with warm water
- Gently wipe across your lashes and lid margin
- Rinse with cool water
- Gently massage the outer eyelids